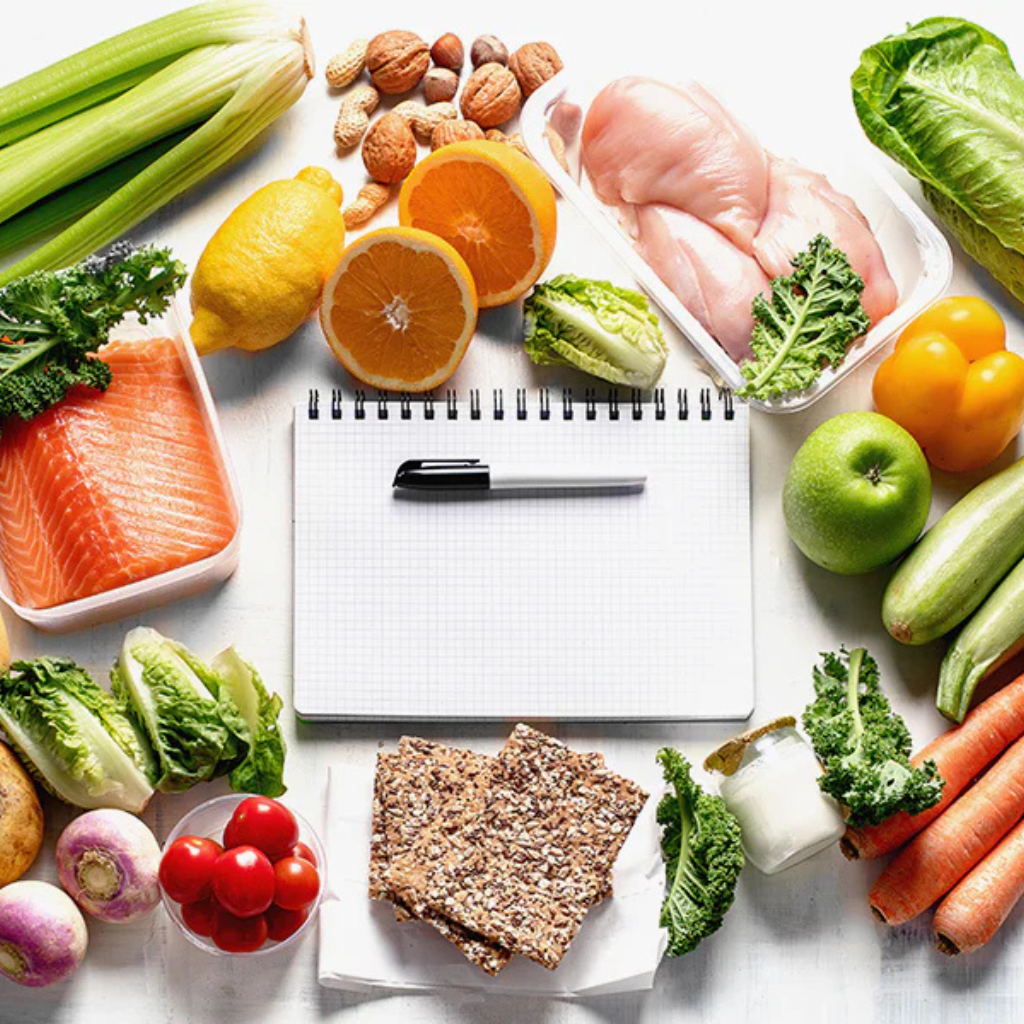
Choosing the right diet plan is one of the most important decisions you can make for your health and well-being. A well-designed diet plan can help you reach your health goals, whether it’s weight loss, improving energy levels, managing chronic conditions, or enhancing athletic performance. However, with so many options available, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. The key to success lies in understanding that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. What works for one person may not work for another, which is why selecting a diet plan that aligns with your specific needs and lifestyle is crucial.
A personalized approach to dieting takes into account various factors such as your unique health goals, daily routine, food preferences, and body’s nutritional requirements. Unlike generic diets that might offer temporary results, a customized plan focuses on what’s sustainable and beneficial for you in the long term. This personalized strategy not only helps you achieve better results but also ensures you stay motivated and maintain those results over time. When you tailor your diet to fit your specific circumstances, you’re more likely to make lasting changes that contribute to overall health and well-being.
Your Health Goals
When choosing the right diet plan, the first step is to clearly define your health goals. These goals serve as the foundation for selecting a plan that suits your needs. The more specific and realistic your goals are, the easier it will be to choose the best approach for achieving them. Your health goals may vary depending on what you want to achieve in the short-term and long-term. Common goals include weight loss, muscle gain, improving overall health, or managing certain health conditions.
- Weight Loss: If your primary goal is to lose weight, your diet plan should focus on creating a calorie deficit, meaning you consume fewer calories than you burn. This requires careful attention to portion sizes, nutrient-dense foods, and balancing macronutrients to ensure you’re still meeting your body’s nutritional needs while losing weight. Common diets for weight loss include low-calorie, low-carb, or intermittent fasting plans.
- Muscle Gain: For those aiming to build muscle, the focus shifts to consuming more calories, with an emphasis on protein intake to support muscle repair and growth. Strength training and resistance exercises also play a key role in muscle gain. A high-protein diet, rich in healthy fats and complex carbohydrates, is essential to fuel workouts and promote muscle recovery.
- Overall Health: If your goal is to improve your general health and maintain a balanced lifestyle, a diet that focuses on a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, is ideal. This approach helps maintain a healthy weight, supports energy levels, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. Diets like the Mediterranean diet or the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet are excellent for overall health.
- Chronic Condition Management: Some individuals may need a diet plan to manage specific health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease. In this case, your diet will need to support managing these conditions, focusing on foods that regulate blood sugar, lower cholesterol, or reduce inflammation. For example, a low-sodium, high-fiber diet can be beneficial for managing blood pressure, while a balanced carb intake is crucial for managing diabetes.
Understanding how diet affects different goals is essential for crafting a diet plan that works for you. The right diet plan will fuel your body to achieve your specific objectives while ensuring you receive the necessary nutrients for overall well-being. Whether your goal is weight loss, muscle gain, or improving your health, choosing a diet that supports your unique needs will set you up for long-term success.
Lifestyle and Daily Routine
When selecting the right diet plan, it’s essential to consider how your daily routine, work schedule, and lifestyle habits will impact your ability to follow a diet consistently. A diet plan that doesn’t align with your routine can quickly become unsustainable. By understanding your day-to-day commitments and incorporating them into your diet plan, you’re more likely to stick with it over the long term.
The Role of Your Schedule
Your work schedule, family commitments, and personal habits all play a significant role in how practical and manageable a diet plan will be. If you work long hours, for instance, a diet plan that requires frequent meal preparation or specialized ingredients might be challenging to maintain. On the other hand, if you have a flexible schedule or work from home, you may have more time to dedicate to meal prep and cooking from scratch. Understanding this balance is key to choosing a diet that fits seamlessly into your life.
- Work: If you have a busy or unpredictable work schedule, it may be difficult to stick to a diet that requires multiple meals a day or elaborate cooking. In this case, you may prefer a diet that allows for flexibility, such as intermittent fasting, or one that includes meal prepping in bulk to save time. You might also want to consider portable, easy-to-prepare meals that fit into your workday, like salads, wraps, or smoothies.
- Family Life: If you have a family, choosing a diet that works for everyone is important. A restrictive or highly specialized diet can create tension or lead to unnecessary stress when it doesn’t align with family meals. Selecting a plan that can be easily adapted for both your needs and your family’s preferences—such as a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods—is often a better approach.
- Exercise Habits: Your diet should complement your exercise routine. If you’re highly active and engage in strength training or endurance sports, you’ll need a diet that supports energy levels and aids in muscle recovery. If you have a sedentary lifestyle or only perform light exercise, a more moderate approach to calories and macronutrients may be sufficient. Factor in your typical exercise intensity and frequency when selecting a diet, as your body’s energy demands will change based on your activity level.
Considerations for Time Management and Meal Prep
Time management plays a vital role in successfully sticking to a diet. If your schedule is hectic, meal planning and prepping in advance can save you time and reduce the temptation to skip meals or resort to unhealthy takeout. Planning your meals ahead of time helps you stay on track and makes healthy eating more accessible, even on busy days.
- Meal Prep: Consider dedicating a specific day, such as the weekend, to meal prep. You can batch-cook meals or chop vegetables in advance, so your meals are ready to go throughout the week. This can be particularly helpful for people on weight-loss plans or those following a strict eating schedule, as it helps maintain portion control and ensures you’re not reaching for convenience foods that might derail your progress.
- Quick and Easy Options: If you don’t have the time for extensive meal prep, look for simple, quick recipes that require minimal cooking time but still align with your dietary goals. Pre-packaged healthy meals or ingredients that require little preparation, like pre-washed salad greens, microwaveable grains, or frozen vegetables, can also save time while keeping your diet balanced.
By understanding how your schedule, family dynamics, and exercise habits influence your diet plan, you can select a strategy that fits effortlessly into your routine. Balancing your diet with time-efficient meal prep and flexibility can make all the difference in achieving your health goals without feeling overwhelmed. The key is to create a plan that works with your lifestyle, not against it.
Nutritional Needs
When selecting the right diet plan, understanding your body’s specific nutritional needs is crucial for achieving your health goals while maintaining overall well-being. Every individual has unique dietary requirements based on factors such as age, gender, activity level, medical conditions, and personal goals. By identifying these needs and ensuring your diet plan meets them, you can enhance your energy levels, improve your health, and better manage your weight or fitness.
Identifying Your Body’s Specific Nutritional Requirements
To begin, it’s important to understand that your body requires a range of nutrients to function properly, including vitamins, minerals, water, and, most notably, macronutrients (proteins, fats, and carbohydrates). The amount and balance of these macronutrients vary depending on your individual needs and goals.
- Age and Gender: Nutritional requirements change as you age, with increased needs for certain nutrients at different life stages. For example, children, teenagers, and pregnant women have higher nutritional demands, while older adults may require more of certain vitamins and minerals to maintain bone health and prevent chronic diseases. Men and women may also have differing caloric and macronutrient needs due to differences in muscle mass and metabolism.
- Activity Level: If you’re highly active or engage in regular physical activity, your calorie and macronutrient needs will be higher to support energy expenditure and muscle recovery. For example, athletes often require more protein to aid muscle repair and may also need more carbohydrates for energy. Sedentary individuals, however, may need fewer calories and should focus on maintaining a balanced intake of essential nutrients without excess.
- Health Conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or gastrointestinal disorders, may require specialized diets to manage symptoms and improve overall health. For example, individuals with diabetes must monitor carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar levels, while those with heart disease might need a low-sodium, heart-healthy diet rich in fiber and healthy fats. If you have any underlying health issues, it’s important to tailor your diet to meet these specific needs.
Importance of Balancing Macronutrients
Macronutrients, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are the building blocks of your diet and play key roles in maintaining energy levels, supporting body functions, and helping you reach your health goals. Each macronutrient has a unique function, and achieving a balance that aligns with your goals is essential for optimal health.
- Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. Protein is especially important if your goal is to build muscle or recover from exercise. Sources of high-quality protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, beans, legumes, and plant-based proteins like tofu or tempeh. Depending on your goals, protein intake typically ranges from 10-35% of your total daily calories.
- Fats: While fats are often avoided in many diets, they are a crucial part of a healthy diet, providing a concentrated source of energy and supporting cell structure, brain function, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Healthy fats should come from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish (like salmon). Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats, which can contribute to heart disease. Fats should make up about 20-35% of your daily caloric intake, depending on your goals.
- Carbohydrates: Carbs are the body’s primary source of energy, fueling your brain, muscles, and organs. They are particularly important if you’re engaging in high-intensity exercise. Carbohydrates should ideally come from complex sources, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, as they provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Simple carbohydrates, found in sugary foods and drinks, should be limited. Depending on your activity level and goals, carbs can make up anywhere from 40-60% of your daily calories.
Tailoring Your Macronutrient Balance
The right balance of macronutrients varies from person to person and largely depends on your specific health goals. For example, if you’re focused on weight loss, you might reduce your carbohydrate intake to promote fat burning, while ensuring you get enough protein to maintain muscle mass. On the other hand, if you’re trying to gain muscle, you may prioritize protein intake and increase overall calorie consumption, including a balanced amount of carbohydrates to fuel your workouts.
By understanding your body’s unique nutritional needs and the importance of balancing proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, you can create a diet plan that provides the right fuel for your daily activities and supports your long-term health goals. Ensuring you’re consuming the right amount of each macronutrient will not only optimize your physical performance but also improve your overall health and well-being.
Dietary Preferences and Restrictions
When selecting a diet plan, it’s important to consider your personal food preferences, as well as any dietary restrictions you may have. A diet that aligns with your tastes and lifestyle not only makes it easier to stick to your plan but also helps ensure that you enjoy the foods you eat, making your journey toward better health more sustainable. At the same time, it’s crucial to take any allergies or intolerances into account, as avoiding these foods will prevent potential adverse reactions and contribute to better overall health.
Managing Food Preferences
Many people choose specific diets based on personal values, ethical beliefs, or cultural practices. Common food preferences include vegetarian, vegan, and gluten-free diets, but there are many others based on individual needs or desires. When considering these preferences, it’s important to select a diet plan that is flexible enough to allow you to meet your nutritional needs while adhering to your food choices.
- Vegetarian and Vegan Diets: A vegetarian diet excludes meat and poultry, while a vegan diet eliminates all animal products, including dairy and eggs. Both of these diets can provide numerous health benefits, such as reduced risk of heart disease and cancer, but they require careful planning to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients. Vegans, for instance, may need to supplement with vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are typically found in animal products. It’s essential to choose plant-based sources of protein, such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa, as well as to ensure you’re consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts to meet your nutritional needs.
- Gluten-Free Diet: A gluten-free diet excludes wheat, barley, and rye, making it essential for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. While this diet can help alleviate symptoms like digestive distress and fatigue, it requires attention to food labels and a focus on naturally gluten-free foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and gluten-free grains like rice, quinoa, and corn. It’s also important to ensure that processed gluten-free foods, which are often high in sugar or fat, are consumed in moderation.
- Other Preferences: Other dietary preferences may include pescatarian (fish and seafood-based), paleo (emphasizing whole foods and excluding processed foods), or Mediterranean (rich in fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, and lean proteins). When selecting a diet, it’s vital to choose one that is nutritionally balanced, accommodates your food preferences, and supports your health goals.
Addressing Allergies or Intolerances
Food allergies and intolerances are another important consideration when choosing a diet plan. These conditions can cause a range of symptoms, from mild digestive issues to severe allergic reactions. Identifying and managing allergies or intolerances is critical for avoiding negative health effects and ensuring your diet remains nutritionally complete.
- Food Allergies: Common food allergens include nuts, dairy, shellfish, eggs, soy, and wheat. For individuals with food allergies, a diet plan must be carefully tailored to avoid these allergens while ensuring a balanced intake of other nutrients. For example, individuals allergic to dairy can replace it with plant-based alternatives like almond milk or coconut yogurt. Those allergic to peanuts may need to avoid nut-based proteins and look for alternatives like seeds or legumes.
- Lactose Intolerance: For individuals who are lactose intolerant, consuming dairy products can lead to discomfort such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Lactose-free alternatives, such as lactose-free milk, yogurt, and cheese, can be excellent substitutes. Additionally, many people with lactose intolerance can tolerate small amounts of dairy or opt for fermented dairy products like yogurt, which contain beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion.
- Other Intolerances: Some people may have intolerances to foods such as gluten, fructose, or specific food additives like MSG. Identifying and avoiding these foods is key to managing symptoms, but it’s also important to ensure that your diet remains balanced and rich in essential nutrients. If you have an intolerance, it’s crucial to find suitable substitutes that provide the same nutritional value without triggering symptoms.
When addressing food preferences and restrictions, the key is to choose a diet that allows you to maintain both your health and your lifestyle. By managing your food choices thoughtfully and being aware of your dietary needs and limitations, you can create a plan that supports your health goals while also providing the flexibility to enjoy the foods you love. Proper planning and education about your nutritional requirements are essential in making informed choices that ensure you stay healthy and satisfied with your diet.
Budget and Cost
When choosing the right diet plan, it’s essential to evaluate its affordability, especially since maintaining a healthy eating routine can sometimes feel costly. However, a diet plan doesn’t have to be expensive to be effective. By considering your budget and understanding how to meal plan smartly, you can follow a nutritious diet that fits within your financial constraints. Here are some strategies for evaluating costs and meal planning on a budget.
Evaluating the Affordability of Different Diet Plans
Diet plans can vary significantly in cost depending on the types of foods they emphasize. Some diets, like the Mediterranean or paleo diets, may rely on premium ingredients, such as organic produce, lean meats, and specialty items, which could increase the overall cost. On the other hand, plant-based or whole-food diets, when planned effectively, can be more budget-friendly. Here are some factors to consider when evaluating the cost of a diet plan:
- Grocery Store vs. Prepared Meals: Some diet plans promote the use of prepared or pre-packaged meals, which can be convenient but often come at a premium price. Meal delivery services or packaged diet plans might seem convenient, but they can quickly add up. Preparing meals at home using whole foods is generally more affordable and allows you to control portion sizes, ingredients, and overall costs. Cooking in bulk and using leftovers can further reduce costs while ensuring that you maintain the quality of your diet.
- Specialty Ingredients: Some diets require specialty ingredients that may be more expensive, such as organic produce, grass-fed meats, or dairy-free alternatives. If you’re on a tight budget, it’s a good idea to research where you can purchase these ingredients at lower prices. For example, shopping at local farmers’ markets, bulk food stores, or looking for sales can help lower costs. Additionally, many of these specialty ingredients can be substituted with more affordable options without compromising nutritional value. For instance, non-dairy milk can be replaced with cheaper alternatives like oats or soy milk, and organic produce can often be swapped for conventionally grown options without a significant nutritional difference.
- Supplements: Some diet plans, particularly those focusing on weight loss or bodybuilding, may recommend supplements (such as protein powder, vitamins, or other specialty products). While supplements can be useful, they often increase the cost of the diet. It’s important to assess whether these supplements are truly necessary or if you can get the nutrients from whole foods instead. For example, a balanced diet with a variety of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins will usually provide all the vitamins and minerals you need without the need for expensive supplements.
Meal Planning on a Budget
Meal planning is one of the best strategies for keeping costs low while following a nutritious diet. When you plan your meals in advance, you can avoid impulse purchases and waste, ensuring that every ingredient you buy gets used. Here are some tips for meal planning on a budget:
- Plan Meals Around Affordable Staples: Base your meals around budget-friendly staples that are rich in nutrients. Items like beans, lentils, rice, potatoes, oats, and pasta are inexpensive and versatile. These staples can form the foundation of many meals, allowing you to add variety with vegetables, lean proteins, or sauces to keep things interesting. Frozen vegetables are a great option, as they are often more affordable than fresh produce and have a longer shelf life without losing much nutritional value.
- Batch Cooking and Meal Prep: Batch cooking and meal prepping are great ways to save both time and money. When you cook large batches of food, you can freeze portions for later use, ensuring that you always have healthy meals available when you’re busy or don’t feel like cooking. This reduces the temptation to order takeout or buy more expensive ready-made meals. Dishes like stews, soups, casseroles, and stir-fries are excellent for meal prep because they store well and can be easily reheated.
- Shop Smart: Shopping smart can significantly cut down on costs. Make a weekly grocery list based on your meal plan to avoid purchasing unnecessary items. Take advantage of sales, discounts, and coupons, and consider buying in bulk for commonly used ingredients, like rice, oats, and canned beans. Also, try to buy seasonal fruits and vegetables, as they tend to be more affordable and fresher. If possible, opt for store brands, which are often just as good as name-brand products but come at a lower price.
- Minimize Food Waste: One of the biggest challenges when managing a food budget is reducing waste. By using leftovers creatively (e.g., turning yesterday’s roast chicken into chicken soup or using veggie scraps for broth), you’ll not only stretch your meals further but also ensure that you’re getting the most out of your grocery budget. Storing food properly and understanding portion sizes can also help prevent waste.
Maintaining a healthy diet on a budget is entirely possible with thoughtful planning. By evaluating the costs of different diet plans, focusing on affordable staples, planning meals ahead of time, and being mindful of food waste, you can stay on track with your health goals while keeping your finances in check. The key is to find a balance between eating nutritious foods and being resourceful with your shopping habits. This way, you can nourish your body without breaking the bank.
Sustainability and Flexibility
When selecting a diet plan, sustainability and flexibility are two crucial factors that determine whether you will successfully adhere to the plan over the long term. While it’s important to choose a diet that aligns with your health goals, it’s equally important to ensure that the diet is realistic and adaptable to your lifestyle. A sustainable diet is one that you can maintain over time without feeling deprived or overwhelmed, while flexibility allows you to make adjustments as your needs and circumstances evolve. Let’s explore how to choose a diet that is both sustainable and flexible for long-term success.
Choosing a Diet That Is Easy to Stick With Long-Term
Many people begin a diet with the best of intentions, but without a plan that is sustainable, it’s easy to fall off track. A diet plan that feels restrictive or overly complicated can lead to frustration and burnout, which makes it difficult to stick with over time. Here are some ways to ensure your chosen diet is sustainable:
- Ease of Meal Preparation: A diet plan that requires hours of preparation and expensive ingredients may not be sustainable in the long run. Choose a plan that allows for simple, quick meals and doesn’t require too much time or effort to maintain. For example, preparing meals in batches or utilizing easy-to-make recipes can save you time and effort throughout the week, making it easier to stick with your plan.
- Enjoyment of Food: If you dislike the foods included in your diet, it’s going to be difficult to stay committed. A sustainable diet is one that incorporates foods you enjoy and that fit your taste preferences. Rather than eliminating foods entirely, consider a balanced approach that allows you to eat the foods you love in moderation while still meeting your health goals. For example, if you’re following a low-carb plan but love pasta, you can experiment with alternative options like zucchini noodles or whole-grain pasta.
- Realistic Portions and Flexibility: Extreme calorie restriction or overly rigid portion control can make a diet unsustainable. Focus on adopting a plan that encourages balanced meals with appropriate portion sizes, rather than drastically reducing calories. When the diet feels more balanced and less like a restrictive regimen, it’s easier to stay motivated and committed over time. Including occasional treats or “cheat meals” can help you maintain mental and emotional satisfaction without derailing your progress.
Understanding the Importance of Flexibility and Adaptability in Your Plan
Flexibility is key to maintaining long-term success with a diet plan, as life can change and require adjustments to your eating habits. Whether due to a change in work schedule, travel, or personal preferences, being able to adapt your diet to new circumstances will keep you on track. Here’s why flexibility matters:
- Adapting to Lifestyle Changes: Life events, such as a new job, a move, or a change in family dynamics, can affect your daily routine and eating habits. A flexible diet plan allows you to adjust your meals and approach as needed. For example, if you find yourself working longer hours and unable to prepare meals from scratch every day, a flexible plan might include healthy store-bought options or meal delivery services. The key is to ensure that even with these adjustments, your diet still aligns with your overall health goals.
- Dealing with Social Situations: Social events like family gatherings, parties, or dining out can make sticking to a strict diet challenging. A flexible diet plan allows for occasional indulgences without guilt or feeling like you’ve failed. The ability to adapt and enjoy food in social settings while still maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for long-term success. For instance, if you’re following a low-carb diet but are invited to a birthday party with cake, flexibility allows you to have a slice without derailing your progress. This approach helps maintain a positive relationship with food.
- Tuning Into Your Body’s Needs: Flexibility also means being able to listen to your body’s signals and adjusting your diet as necessary. For example, if you feel overly fatigued on a specific plan, you might need to increase your intake of certain nutrients, such as proteins or healthy fats. Alternatively, if you feel too full or bloated, you might adjust your portion sizes or consider modifying the types of foods you eat. A diet that allows room for these adjustments can help prevent feelings of frustration and allow you to stay on course while maintaining your health.
Choosing a diet that is both sustainable and flexible is crucial for long-term success. A sustainable diet is one that fits seamlessly into your life, is enjoyable, and allows for realistic portion sizes and balance. Flexibility enables you to adapt to changes in your lifestyle, social situations, and personal preferences while still adhering to your health goals. By selecting a diet plan that you can maintain over time and that allows for adjustments as needed, you are setting yourself up for lasting success and a healthier, more fulfilling lifestyle.
Support and Guidance
When choosing a diet plan, seeking support and guidance from reliable sources can play a significant role in achieving long-term success. A well-structured diet plan, combined with professional advice and external support, can make navigating the challenges of adopting a new eating regimen much easier. Whether it’s through consulting experts or leveraging community resources, having a support system helps ensure you stay on track and make informed decisions.
The Value of Professional Advice (e.g., Nutritionists, Dietitians)
Consulting with a nutritionist or dietitian can provide personalized insights into your nutritional needs, health goals, and dietary preferences. These professionals are trained to offer advice based on scientific evidence and can help you choose the right diet plan that best suits your unique requirements. Here’s why professional guidance is valuable:
- Personalized Plans: Nutritionists and dietitians take into account your individual health history, lifestyle, and goals when recommending a diet. They can help identify specific nutritional needs and provide tailored advice that considers any existing health conditions (e.g., diabetes, food allergies, or heart disease). This personalized approach increases the likelihood of success compared to following a generic diet plan.
- Nutritional Balance: A dietitian can guide you on how to balance macronutrients (proteins, fats, carbs) and micronutrients (vitamins, minerals) to ensure you are meeting your body’s needs. They can also help you avoid nutrient deficiencies and educate you on how to make healthier food choices while still enjoying a variety of meals.
- Long-term Success: Professional advice isn’t limited to helping you get started with a diet. Dietitians and nutritionists can offer ongoing support, helping you adjust your plan as needed and address any obstacles you encounter. They are also equipped to provide guidance on maintaining healthy habits long after you’ve reached your goal.
The Role of Online Resources, Communities, and Accountability Partners
In addition to professional advice, online resources, communities, and accountability partners can significantly enhance your journey toward achieving your health goals. These resources offer guidance, support, and motivation when you need it most. Here’s how:
- Online Resources: The internet offers a wealth of information on diets, meal planning, recipes, and success stories. Websites, blogs, apps, and YouTube channels can provide useful tips and inspiration, as well as connect you with like-minded individuals following similar dietary paths. However, it’s important to ensure the resources you use are credible and backed by scientific evidence.
- Online Communities: Joining online communities such as social media groups, forums, or specialized diet platforms allows you to engage with others who share similar health goals. These communities provide a space to ask questions, share experiences, and gain support. Being part of a group can help you stay motivated and accountable, especially on days when you feel discouraged.
- Accountability Partners: Having someone to share your journey with can make a significant difference in staying on track. An accountability partner can be a friend, family member, or fellow dieter who helps keep you motivated and committed to your plan. Regular check-ins, progress updates, and mutual encouragement foster a sense of responsibility and connection, which can lead to improved adherence and better results.
Tracking and Adjusting Your Plan
As you progress with your diet, monitoring and adjusting your plan is essential for achieving lasting results. Tracking your progress allows you to assess how well the plan is working for you, while making necessary adjustments ensures that your approach continues to meet your body’s evolving needs.
The Importance of Monitoring Progress
Tracking your progress is a key component of staying motivated and ensuring that you’re on the right path toward your health goals. Regular monitoring provides insight into how your diet is impacting your body and helps you stay focused. Here’s why tracking is important:
- Assessing Effectiveness: By tracking metrics such as weight, body measurements, energy levels, or specific health markers (e.g., blood pressure, cholesterol), you can gauge whether the diet is achieving the results you desire. If progress is slower than expected, tracking can highlight potential adjustments or areas that need improvement.
- Identifying Patterns: Monitoring allows you to identify patterns in how your body responds to certain foods, meals, or macronutrient ratios. For example, if you notice that you feel more energized on days when you consume more protein or have a better mood when you eat balanced meals, this information can guide your future choices.
- Staying Accountable: Keeping track of what you eat, how much you eat, and how you feel afterward can hold you accountable to your goals. Tracking can serve as a reminder of your commitment and reinforce positive behaviors. Using apps, journals, or spreadsheets to log your meals and progress helps create a visual representation of your achievements.
Adjusting Your Plan as Your Body Responds
As you monitor your progress, it’s important to remain flexible and adjust your diet plan according to how your body responds. Everyone’s body is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. Here’s how to adjust your plan effectively:
- Reevaluating Goals: Over time, your goals might evolve. For example, if you initially set a weight loss goal but now want to focus on improving muscle tone or increasing energy levels, you may need to adjust your diet accordingly. As your body adapts to the initial changes, the plan that worked at the beginning might require tweaks to continue progressing.
- Modifying Macros: As your body adapts, you might find that you need to adjust the balance of macronutrients in your diet. If you’ve hit a plateau or your energy levels are low, it might help to shift your carbohydrate or fat intake, or increase protein to support muscle growth. Regular adjustments based on your body’s signals ensure that your diet continues to meet your needs.
- Addressing Obstacles: If you encounter challenges—such as feelings of fatigue, irritability, or digestive issues—it’s important to reassess your plan. These signs could indicate that you need to make adjustments, whether that’s increasing your fiber intake, changing meal timing, or addressing food sensitivities. A flexible approach allows you to listen to your body and make changes that promote well-being.
Support and guidance, coupled with regular tracking and adjustments, are key elements in ensuring the success of any diet plan. Professional advice provides personalized insights, while online communities and accountability partners offer valuable support. By monitoring your progress and making adjustments as needed, you can optimize your diet plan to meet your health goals and achieve lasting, sustainable success.
Read more: IGF-1 LR3 Before and After: Understanding the Impact on Body Composition
Conclusion
Choosing the right diet plan is a personal journey that involves understanding your unique health goals, lifestyle, and preferences. There is no one-size-fits-all approach, and what works for someone else may not necessarily work for you. By considering factors such as your specific health goals, nutritional needs, lifestyle, and any dietary restrictions or preferences, you can select a plan that is not only effective but also sustainable in the long term.
Support and guidance from professionals, like nutritionists and dietitians, as well as resources from online communities and accountability partners, can provide the structure and motivation needed to stay on track. Additionally, regularly tracking your progress and being open to adjusting your plan as your body responds are essential for making continuous improvements and achieving lasting results.
Ultimately, the right diet plan for you is one that aligns with your goals, fits seamlessly into your lifestyle, and is flexible enough to adapt to your evolving needs. By focusing on long-term success rather than quick fixes, you’re setting yourself up for a healthier, more balanced life. Remember, consistency, patience, and a personalized approach are key to achieving the best results and maintaining a positive relationship with food and your health.