Embarking on the journey of building your dream home is an exciting milestone, but it’s essential to recognize that nature often shares the land you plan to develop. Among the many species you may encounter, bats hold a particularly important place in our ecosystem. These fascinating creatures serve as natural pest controllers, consuming thousands of insects each night, including mosquitos and agricultural pests, which helps maintain ecological balance.
In the UK, bats are legally protected due to their ecological importance and declining populations. Laws such as the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 and the Conservation of Habitats and Species Regulations 2017 make it illegal to harm bats, disturb their roosts, or disrupt their habitats. This protection applies regardless of whether bats are actively present or not, emphasizing the need for careful planning and compliance when building on land that might host these creatures.
Addressing the presence of bats before starting construction is not just a legal requirement—it’s a vital step toward ensuring the harmony between human development and wildlife conservation. Taking the time to identify and accommodate bats on your land can prevent costly delays, protect biodiversity, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Understanding how to manage this process responsibly is the first step in turning your dream home into a reality while respecting the environment.
Understanding Bats in the UK
How Many Species of Bats Are There?
The UK is home to 17 species of bats, all of which are fascinating and vital to the environment. These species vary in size, behavior, and habitat preferences, but they share a common role as crucial players in maintaining ecological balance. Among the most commonly encountered is the pipistrelle bat, a small and agile species known for its reddish-brown fur. Pipistrelles are widespread across the UK and are often seen fluttering through the twilight skies, hunting tiny insects.
Other notable species include the brown long-eared bat, known for its distinctively large ears, and the noctule bat, one of the largest species in the UK. Each species has unique roosting habits and dietary needs, making their conservation a complex yet essential task. Understanding the diversity of bats in the UK highlights their importance and the need to protect their habitats.
Why Are Bats Protected by Law?
Bats play a vital role in pest control and pollination, contributing significantly to agriculture and the natural ecosystem. By consuming vast quantities of insects, they help control pest populations, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Additionally, some bat species act as pollinators, spreading seeds and ensuring the growth of plants and trees. Their contributions make them a cornerstone of a healthy environment.
Recognizing their ecological value, UK laws have been established to protect bats and their habitats. The Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 and the Conservation of Habitats and Species Regulations 2017 ensure that bats are safeguarded from harm. It is illegal to kill, injure, or disturb bats, as well as to damage or destroy their roosts, even if unoccupied. This legal framework reflects the commitment to preserving biodiversity and emphasizes the responsibility of landowners and developers to consider bats during any construction or land development.
Identifying Bat Roosts
Common Bat Roosting Habitats
Bats are incredibly adaptable creatures that roost in a variety of locations, each providing the shelter and darkness they need for resting and raising their young. Common bat roosting habitats include:
- Trees: Bats often roost in natural cavities or under loose bark. Mature or dead trees with cracks, crevices, and hollows are particularly attractive to bats.
- Buildings: Older structures, such as barns, attics, and eaves of houses, are common roosting sites. Bats can enter through small gaps or openings and prefer places where they can hang undisturbed.
- Caves and Mines: Natural caves, disused mines, and similar dark, sheltered locations offer ideal roosting conditions for some bat species.
- Bridges: Some species roost beneath bridges, using the cracks and crevices of the structure.
Understanding where bats are likely to roost helps identify areas of your land that may be of interest to these nocturnal animals, guiding conservation efforts during construction.
Signs of Bat Activity on Your Land
Recognizing the presence of bats is essential for planning your construction project responsibly. Signs of bat activity include:
- Droppings: Bat droppings resemble mouse droppings but crumble into a fine powder when crushed, as they are composed of insect remains. These are often found beneath roosting sites.
- Grease Marks: Bats often leave greasy stains or smudges around entry and exit points, caused by their fur brushing against surfaces.
- Chirping Sounds: High-pitched chattering or squeaking noises can sometimes be heard near roosts, particularly during the evening as bats prepare to leave.
- Sightings: Spotting bats flying at dusk or dawn, especially in consistent patterns, can indicate a nearby roost.
If you observe these signs, it’s important to consult a bat surveyor to confirm the presence of bats and determine the next steps. Identifying bat roosts on your land not only ensures compliance with the law but also enables you to take measures to protect these essential members of the ecosystem.
Legal and Environmental Considerations
When embarking on a construction project in the UK, understanding the legal and environmental implications of encountering bats is crucial. These considerations ensure compliance with the law and help protect the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Laws Related to Bat Protection in the UK
Bats and their habitats are strictly protected under various laws, including:
- The Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981: This law makes it illegal to harm or disturb bats or their roosts, regardless of whether they are occupied at the time.
- The Conservation of Habitats and Species Regulations 2017 (as amended): This regulation provides additional protection, prohibiting activities such as capturing, injuring, or killing bats, and damaging or destroying their roosts.
- The Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000: This reinforces protection for species like bats by criminalizing intentional or reckless disturbance.
These laws collectively mean that any activity, including construction, that might impact bats requires careful planning and adherence to legal obligations. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties.
The Role of Conservation in Construction Projects
Incorporating conservation into your construction project not only ensures legal compliance but also aligns with ethical responsibility. Conservation measures may include:
- Bat Surveys: Conducted to determine the presence and type of bats on your land. Surveys assess the significance of habitats and recommend mitigation strategies.
- Alternative Roost Creation: If construction impacts an existing bat roost, creating alternative habitats, such as bat boxes or artificial roosts, can minimize disruption.
- Timing Construction Work: Scheduling activities to avoid the breeding season (May to August) or hibernation period (November to March) reduces the risk of harm to bats.
By integrating conservation strategies, construction projects can move forward while respecting the environment.
Potential Consequences of Disturbing Bats or Their Habitats
Ignoring the legal protections for bats can lead to significant consequences:
- Legal Penalties: Disturbing or destroying a bat roost can result in fines of up to £5,000 per bat or six months’ imprisonment.
- Project Delays: Discovering bats without prior surveys can halt construction until appropriate measures are implemented.
- Environmental Harm: Disturbing bats disrupts their role in controlling insect populations and pollination, which has wider implications for biodiversity.
Understanding these legal and environmental considerations underscores the importance of responsible planning. By respecting bats and their habitats, you not only comply with the law but also contribute to the preservation of a vital species in the ecosystem.
Conducting a Bat Survey
A bat survey is an essential step in planning construction if bats are suspected on your land. This process helps identify the presence of bats and their roosting habits while ensuring compliance with UK wildlife laws. Here’s what you need to know about bat surveys and their importance in your construction journey.
Why Bat Surveys Are Essential Before Construction
Bat surveys serve multiple purposes, including:
- Legal Compliance: Since bats and their roosts are protected under UK law, conducting a survey ensures you adhere to regulations and avoid unintentional harm to these creatures.
- Project Planning: Knowing the location and type of bat activity allows you to design your construction project around these habitats, minimizing disruptions.
- Environmental Responsibility: Protecting bats aligns with broader conservation efforts, preserving their role in the ecosystem as pollinators and natural pest controllers.
Without a bat survey, construction activities risk legal penalties, project delays, and environmental damage.
How Bat Surveys Are Conducted and What to Expect
Bat surveys are typically carried out by licensed ecologists and follow a systematic approach:
- Preliminary Roost Assessment:
- This initial phase involves inspecting the land and structures to identify potential bat roosts.
- Ecologists look for physical signs like droppings, stains around entry points, and evidence of flight paths.
- Activity Surveys:
- If potential roosts are found, activity surveys are conducted during specific times of the year when bats are most active (usually May to September).
- Ecologists use equipment like bat detectors and thermal cameras to monitor bat movements and species identification during dawn and dusk.
- Data Analysis and Reporting:
- The collected data is analyzed to determine the species present, the size of the bat population, and the significance of the habitat.
- A detailed report outlines findings and provides recommendations for mitigation measures, if required.
Surveys are conducted in compliance with strict protocols to minimize disturbance to the bats.
Legal Requirements for Bat Surveys
Bat surveys are often a legal requirement for planning applications when bats are suspected on the land. Key legal aspects include:
- Survey Timing: Surveys must be conducted during the active season for accurate results.
- Licensed Surveyors: Only qualified and licensed ecologists can perform these surveys, as handling or disturbing bats without a license is illegal.
- Mitigation Plans: If bats are found, a mitigation strategy must be approved before construction proceeds.
Failing to conduct a bat survey can result in denied planning permissions, project delays, and potential legal action.
What To Do If Bats Are Found
Discovering bats on your land is not the end of your dream home plans—it’s an opportunity to incorporate responsible and lawful adjustments into your project. Here are the steps to take and considerations to keep in mind if bats are found on your property.
Steps to Take Upon Discovering Bats
- Pause Construction Activities
- Immediately halt any construction or land-clearing activities to avoid disturbing the bats or their roosts. This precaution ensures you comply with legal protections for bats and minimizes stress on the animals.
- Seek Expert Advice
- Engage a licensed bat surveyor or ecologist to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the bats’ presence and habitat.
- Specialists can determine the species, the size of the colony, and the significance of the roost, which are crucial for planning mitigation measures.
- Notify Local Authorities if Required
- In some cases, local planning authorities may need to be informed about the discovery of bats.
- This step ensures your project remains transparent and aligns with legal requirements.
Consulting with Specialists
Licensed specialists, such as bat ecologists, play a vital role in managing the presence of bats during construction. Their expertise helps guide you through:
- Developing a Mitigation Plan:
- This may include creating alternative roosts, adjusting construction timelines, or modifying building designs.
- Securing Licenses:
- If your project involves activities that could disturb bats or their habitats, you’ll need a mitigation license from the relevant authority (e.g., Natural England).
- Monitoring and Compliance:
- Ecologists often oversee construction to ensure all measures are effectively implemented and that no harm comes to the bats.
Adjusting Construction Plans to Accommodate Bat Habitats
When bats are found, modifications to your building plans may be necessary to preserve their habitats:
- Provide Alternative Roosts
- Install bat boxes on trees or structures near the construction site to offer a safe and appealing alternative.
- Ensure these roosts are located in quiet, shaded areas with access to insects for feeding.
- Modify Building Designs
- Incorporate bat-friendly features into your designs, such as bat access points in roofs or bat bricks in walls.
- Use low-impact lighting to avoid disrupting bats’ nocturnal activities.
- Timing Construction
- Schedule disruptive activities outside of key bat seasons, such as breeding (summer) and hibernation (winter), to minimize disturbance.
- Preserve Natural Habitats
- Retain mature trees, hedgerows, and vegetation that provide food and shelter for bats.
- Plan landscaping to enhance biodiversity, creating an environment that supports both bats and other wildlife.
Protecting Bats During Construction
During construction, taking proactive steps to protect bats ensures compliance with the law and supports their conservation. Here’s how you can minimize disruptions while building your dream home.
Ensuring Roosts Are Not Disturbed
- Identify and mark areas where bat roosts are located to prevent accidental disturbance.
- Avoid sealing off or demolishing structures or trees with active roosts unless mitigation measures are in place.
- Limit noise, vibration, and light pollution near roosting sites, especially during breeding and hibernation seasons.
Temporary Measures: Fencing, Netting, or Monitoring
- Fencing: Use protective fencing around bat roosts to restrict access to these areas during construction.
- Netting: Install netting or other barriers to ensure roosts remain undisturbed and prevent access to unfinished structures.
- Monitoring: Hire an ecologist to monitor the site and ensure mitigation measures are effectively implemented throughout construction.
Managing Construction Activities to Minimize Impact
- Plan construction during times of the year when bats are least active (spring and autumn).
- Use bat-friendly lighting solutions, such as low-intensity, downward-facing lights with warm tones, to minimize disruption.
- Regularly communicate with the construction team about the presence of bats and the importance of adhering to protection protocols.
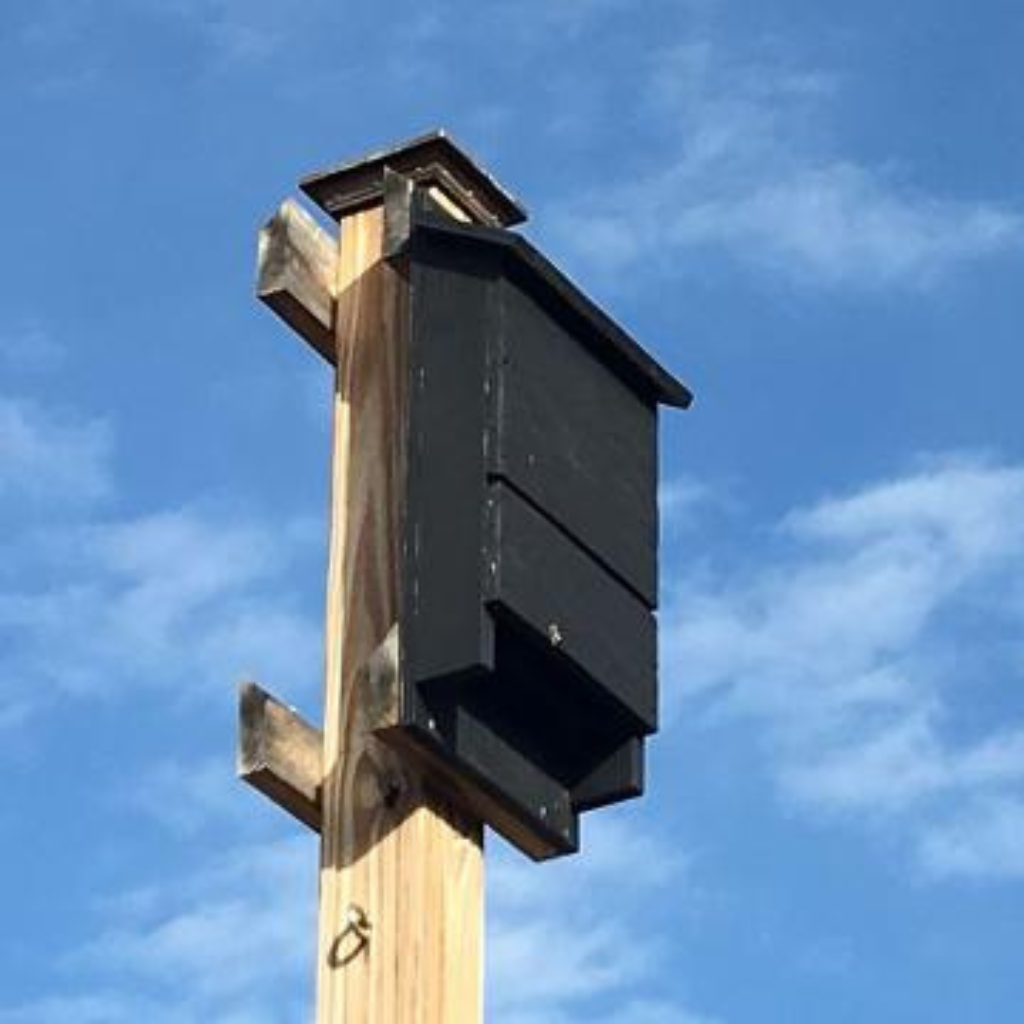
Creating Alternative Roosts and Habitats
If construction requires disturbing existing roosts, creating alternative habitats is essential to support the bat population on your property.
Installing Bat Boxes or Houses on Your Property
- Bat Boxes: Install durable and weather-resistant bat boxes on trees or structures.
- Roof-Based Roosts: Consider bat-friendly features like bat bricks or roof tiles that integrate seamlessly into your building design.
- Placement: Ensure bat houses are installed at least 4-6 meters above ground in shaded areas with minimal disturbance.
Landscaping Tips to Encourage Insects (Bat Food Sources)
- Plant a variety of native flowering plants to attract insects that bats feed on, such as moths and beetles.
- Maintain hedgerows and trees, which serve as foraging pathways for bats.
- Create ponds or water features to encourage insect populations and provide hydration for bats.
Ensuring Alternative Habitats Are Suitable and Sustainable
- Work with an ecologist to design habitats that align with the needs of the bat species on your land.
- Monitor alternative roosts after construction to ensure they are being used and remain in good condition.
- Incorporate long-term maintenance plans to keep the alternative habitats viable for years to come.
Other Protected Species to Consider
In addition to bats, your land may host other protected species. Understanding their needs and legal protections ensures your construction project aligns with environmental regulations.
Overview of Other UK-Protected Species That May Impact Construction
- The UK protects a variety of wildlife to preserve biodiversity and maintain healthy ecosystems.
- Before construction, survey your land for other species that may be present, and consult specialists to manage their conservation.
Specific Examples
- Badgers: Protected under the Protection of Badgers Act 1992, badger setts must not be disturbed without proper licenses.
- Owls: Barn owls and other bird species are protected during nesting seasons. Avoid tree felling or building work that may disturb nests.
- Great Crested Newts: These amphibians are strictly protected under the Conservation of Habitats and Species Regulations. Specific ponds and terrestrial habitats must be preserved or recreated.
- Dormice: Hazel dormice require undisturbed woodland and hedgerows. Construction near their habitats may need careful planning and mitigation.
By recognizing and accommodating these species, you can ensure your project respects all aspects of wildlife conservation.
Read more: Before Hiring, Ask These Questions to Your Real Estate Agent
Conclusion
Building your dream home is an exciting journey, but it comes with a responsibility to protect the environment and the wildlife that calls it home. Bats, as vital members of the ecosystem, require special attention under UK law. From conducting bat surveys to creating alternative habitats, integrating bat-friendly practices into your construction plans ensures compliance and supports biodiversity.
By taking proactive measures to protect bats and other species, you contribute to a sustainable and harmonious relationship with nature. With careful planning and the help of professionals, you can turn your dream home into a reality while preserving the natural beauty and ecological balance of your land.